A Comprehensive Guide of Traditional Timber Formwork
Mar 11, 2025
For decades, traditional timber formwork systems have been a godsend in the construction industry. These systems provide versatile solutions for shaping concrete, from the simplest to the most complex. Whether you are engaged in a small domestic project or large-scale infrastructure, timber formwork techniques ought to be known for effective construction. The details about traditional timber formwork in this guide include its characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and, finally, a comparison between timber formwork and other modern alternatives.
What is Traditional Timber Formwork?
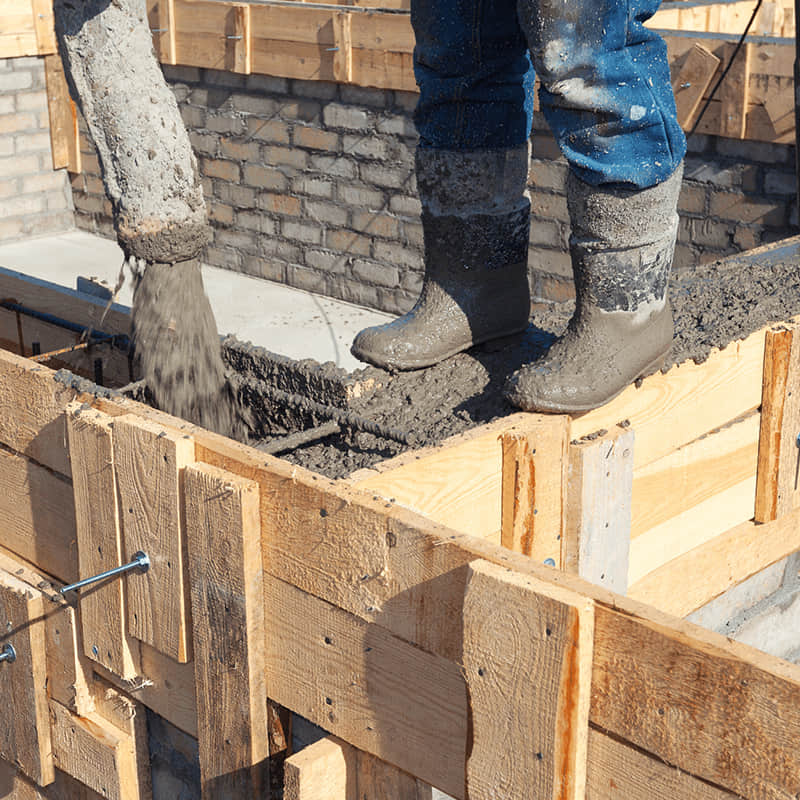
Timber formwork has to do with the use of timber in concrete formwork applications and the assembly of timber shuttering used to create forms that will contain wet concrete until it gets solidified and gains the needed strength. Such formwork has been widely applied as a result of its availability, easy customizability, and better adaptability to complex structures.
Types of Timber Formwork
There are various types of timber for formwork, each suitable for different construction needs:
Traditional Timber Formwork
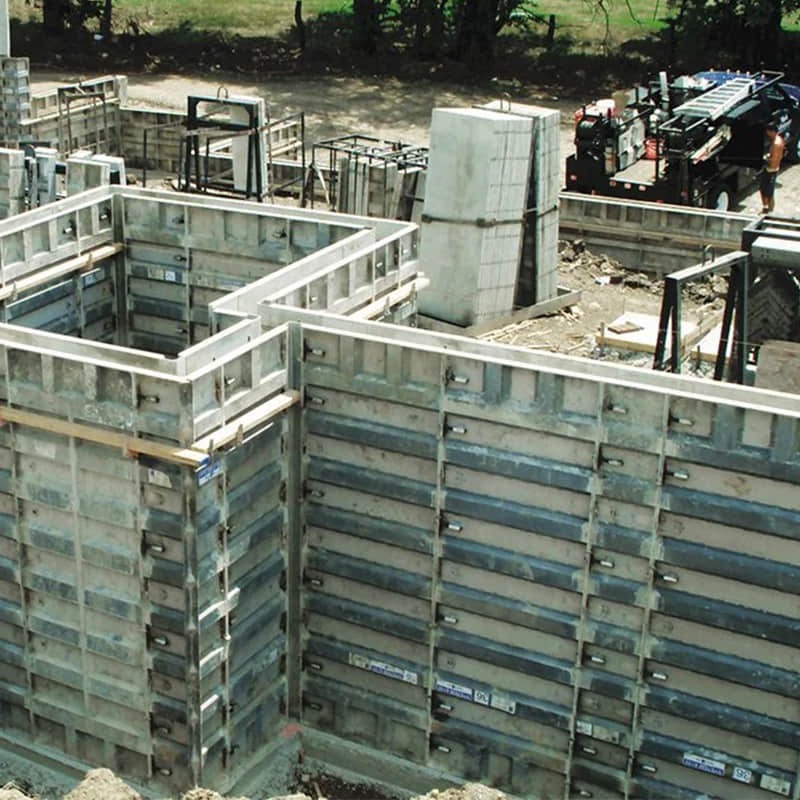
Traditional Timber Formwork is essentially the type of general wood formwork comprising boards and battens. Being the most common type of timber formwork used in construction, this is very cheap and eminently available for use; hence it's most applicable for small construction sites.
However, Traditional Timber Formwork requires manual cutting and assembly, therefore it is more labor-intensive than other forms of timberwork. The very property of wood that is easily modifiable allows also for the traditional timber formwork to be made into irregular and complicated shapes.
Plywood Formwork
Plywood formwork refers to a formwork made From waterproof plywood for surface material and supported by a timber frame. Compared to rough-cut timber, plywood formwork is popular because it gives a much better and smoother concrete finish and can be used regularly many times if properly maintained.
Plywood formwork is generally used for horizontal and vertical structures, such as walls, slabs, and beams.
Beam Formwork
Beam formwork is a formwork system consisting of timber beams, plywood, and supporting elements such as steel or aluminum struts. Compared to traditional timber panels, beam formwork has a higher load-bearing capacity.
Beam formwork is often used in large concrete structures, such as bridges, slabs, and high-rise buildings, and is a reusable and economical option.
Engineered Wood Formwork
With the use of LVL or glulam laminated veneer lumber, the engineered wood formwork is more durable than the usual timber, with better load resistance, stability, and functions of reusability.
Engineered wood formwork is considerably more material-efficient and sustainable than traditional timber and is often used in permanent or semi-permanent structures.
Timber Column Formwork
The timber column formwork is considered to be that formwork of either wood or plywood that is strengthened by using steel or wood frames. It can be easily adjusted for varied column heights and diameters. It's designed for round, square, or rectangular concrete columns and has the ability to provide good strength and support for vertical concrete structures.
Board Formwork
Board formwork is primarily made out of plywood or wood panels supported by wooden joists and beams. It is applied in the construction of horizontal concrete slabs like floors and ceilings.
It is always used together with temporary supports like columns and scaffolding to maintain stability while in use. It is often put into service in residential buildings.
Timber Wall Formwork
Wooden wall formwork consists of wooden profiles, plywood, and supports. It is specific for vertical walls and shear walls project casting.
Formwork made of wood allows for wide flexibility in work regarding wall thickness and height. It is suitable for low-rise to mid-rise building works.
Advantages of Traditional Timber Formwork
Besides the rise of modern formwork concrete systems, traditional timber formwork has gained much popularity in the construction industry whereby it is relatively cheap and readily available. It allows for easy adaptation to various specific needs for which it is used. Among the advantages of profiting from the use of traditional timber formwork, the following are key in building concrete structures:
Economical: Wood is the traditional timber formwork assembly, and this material is available almost everywhere cheaply, providing a low-cost option. In comparison to metal or aluminum formwork, traditional timber has low initial investment costs and is reusable, actually making it a priority option for small to medium-sized jobs.
Easy Handling: Light in comparison with the metal formwork, timber forms should therefore be easy to handle; and transport. Timber formwork is also cuttable, moldable, and assemblable right on site, without specialty tools, simply allowing for adjustments and modifications, therefore making it a straightforward, designable option.
Readily Available Materials: Timber is generally widely available in most parts of the world and easy to procure. One does not need to rely upon specialty suppliers or intricate manufacturing processes, therefore bringing down the overall transportation costs and delivery costs.
Effective Thermal Insulation: Natural wood gives timber so good thermal insulation and helps in regulating the temperature of curing concrete. Meanwhile, in cold weather, it helps to minimize heat loss and avoid quick drying in hot weather, resulting, in turn, in a better concrete finish that corresponds to less cracking and less damage.
Environmentally Friendly: Wood forms may be reused at least several times before being thrown away; thus, it minimizes waste. Wood, unlike metal, is biodegradable, therefore minimizing its impact on the environment.
Disadvantages of Timber Formwork
Timber formwork has largely been used in construction over the years. With advancement in techniques and technology, these timber forms have beencast aside because of their efficiency, durability, and long-term cost efficiency. Here are the main disadvantages:
Limited Reusability and Short Life Cycle: Compared to steel or aluminum alternatives, timber formwork has a relatively short life cycle and may only be used a few times before it requires extensive repairs or even complete discarding. The formwork is drying out through moisture absorption, which causes warping, swelling, and even decay. Frequent repairs and maintenance push expenses higher.
Fragile: Especially under severe weather conditions, timber formwork can split, crack, or shrink easily. Timber formwork cannot endure heavy loads as efficiently as steel or plastic formwork. However, due to loosened nails, screws, and fasteners, the stability of the formwork suffers.
Costlier: Timber formwork, unlike metal formwork, which is prefabricated, is never prefabricated and has to be cut, measured, and assembled on site. This invariably takes more time and hence, costs more for bigger projects.
Fire Hazard: Timber is a flammable material and must present a great fire hazard under some conditions. When being used under high-risk conditions, it has to be fire-retardant treated. It is never advisable to use wooden formwork when fire resistance is required.
Environmental Issues: Excessive encounters with timber can really pose drawbacks in the long run, such as deforestation. If the timber formwork was not derived from sustainable forests, it leaves an ecological footprint.
How to Use and Maintain Timber Formwork?
To increase efficiency, timber shuttering is handled and maintained in the following ways:
Select Quality Timber: proper selection of high-density and well-treated timber increases durability.
Proper Storage: the timber must be kept dry in a well-ventilated area, thus minimizing moisture absorption.
Regular Coating: Formwork oil or release agents should be applied regularly to reduce concrete bonding and prolong its service life.
Ensure Careful Dismantling: proper removal of formworks prevents undue damage and thus facilitates reuse.
Timely Repairs: worn-out sections should be changed, while weak joints should be given reinforcement to extend usability.
Traditional Timber Formwork vs. Modern Formwork Systems
With advancements in concrete formwork, alternative materials such as steel, aluminum, and plastic have gained popularity. Below is a comparison of timber formwork with modern alternatives:
Feature
Traditional Timber Formwork
Modern Formwork (Steel, Plastic, Aluminum)
Cost
Lower upfront cost
Higher initial investment but more durable
Durability
Shorter lifespan
Long-lasting and highly reusable
Customizability
Highly customizable
Prefabricated, less flexible for complex designs
Reusability
Limited reuse cycles
Can be used multiple times
Weight
Lightweight, easy to handle
Heavier, requires lifting equipment
When to Use Traditional Timber Formwork?
The traditional timber concreting systems have been the preferable choice for following instances:
Small to Medium Construction: This is apt for residential projects and foundations, like temporary structures.
Odd and Complex Designs: Timber formwork can easily be shaped into peculiar architectural structures.
Budget Concerns: Timber formwork is a band-aid solution that is friendlier on the budget.
Remote Construction Sites: For areas lacking easy access to modern formwork systems, timber can be more easily transported and erected.
Conclusion
In fact, traditional timber formwork is still one of the popular construction systems used because it is quite affordable, flexible, and available. Comparatively, modem alternatives offer greater durability and are faster and more efficient; yet, timber is and will continue to be an attractive option, particularly for small-scale and customized projects. In trying to availing all timber benefits for efficient concrete formwork applications, the contractor shall choose the right timber for shuttering, ensure it is well-kept, and it has many advantages and limitations.
Would you want to know more about timber shuttering solutions for your endeavor? You may reach out to AJ Building for expert support and quality formwork timber!
FAQ
What are the advantages of using timber formwork?
Cost-effective – cheaper than steel or aluminum formwork.
Easy to cut and assemble – can be modified on-site.
Lightweight – easier to transport and handle.
Good insulation – helps prevent cracking of concrete due to temperature changes.
What to do with old timber formwork?
Reuse it for non-structural purposes, such as scaffolding boards.
Recycle it into wood products such as plywood or particleboard.
Dispose of properly under environmental regulations to minimize waste.
Read More
Unleashing The Top 5 Concrete Formwork Systems ——aS Tuts
Comparison of timber and metal formwork systems ——ResearchGate